Cancer Subtype Clustering
Clustering on Sparse Data in Non-Overlapping Feature Space with Applications to Cancer Subtyping.
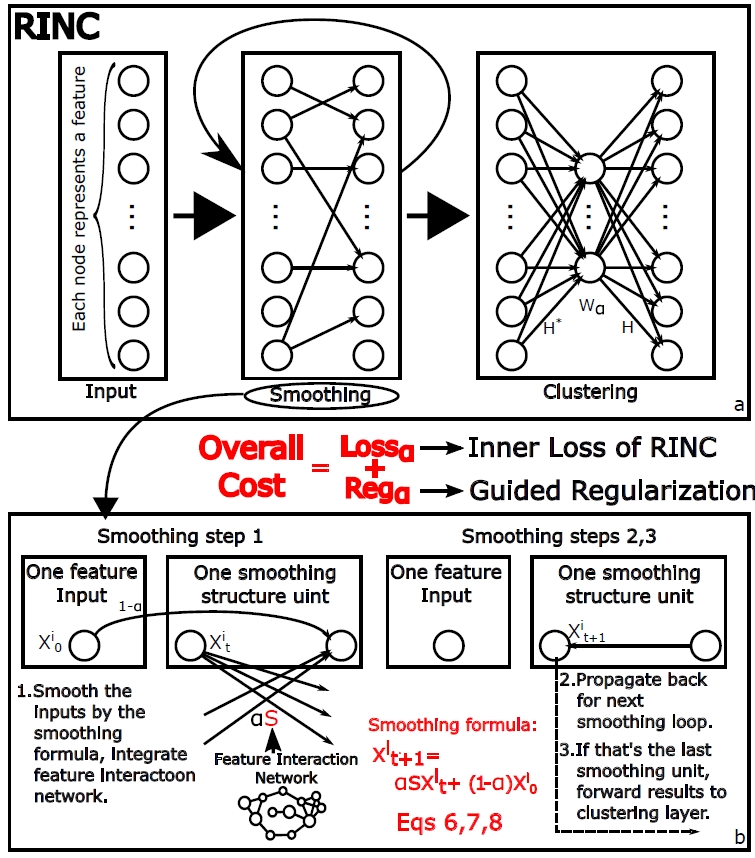
This paper presents a new algorithm, Reinforced and Informed Network-based Clustering (RINC), for finding unknown groups of similar data objects in sparse and largely non-overlapping feature space where a network structure among features can be observed. Sparse and non-overlapping unlabeled data become increasingly common and available especially in text mining and biomedical data mining. RINC inserts a domain informed model into a modeless neural network. In particular, our approach integrates physically meaningful feature dependencies into the neural network architecture and soft computational constraint.